Counting how often items appear in a list is a common programming task.
This challenge asks you to write a function that returns a frequency dictionary, mapping each item to the number of times it occurs.
It’s a simple problem—but one that appears everywhere in real-world code.
Your Task
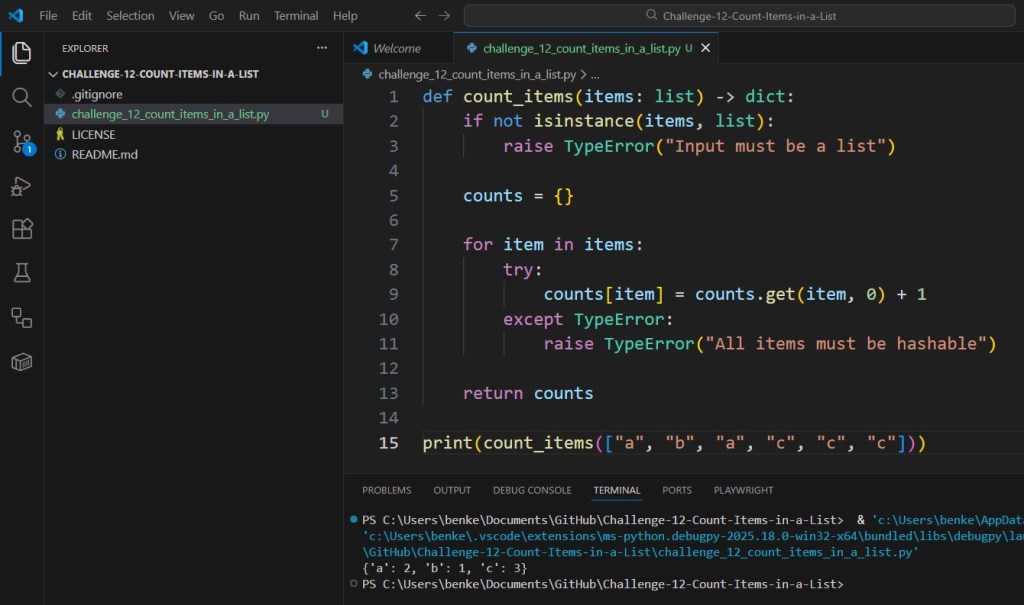
Write a function that counts how many times each item appears in a list.
Function Signature
def count_items(items: list) -> dict:
…
Rules
- The input must be a list.
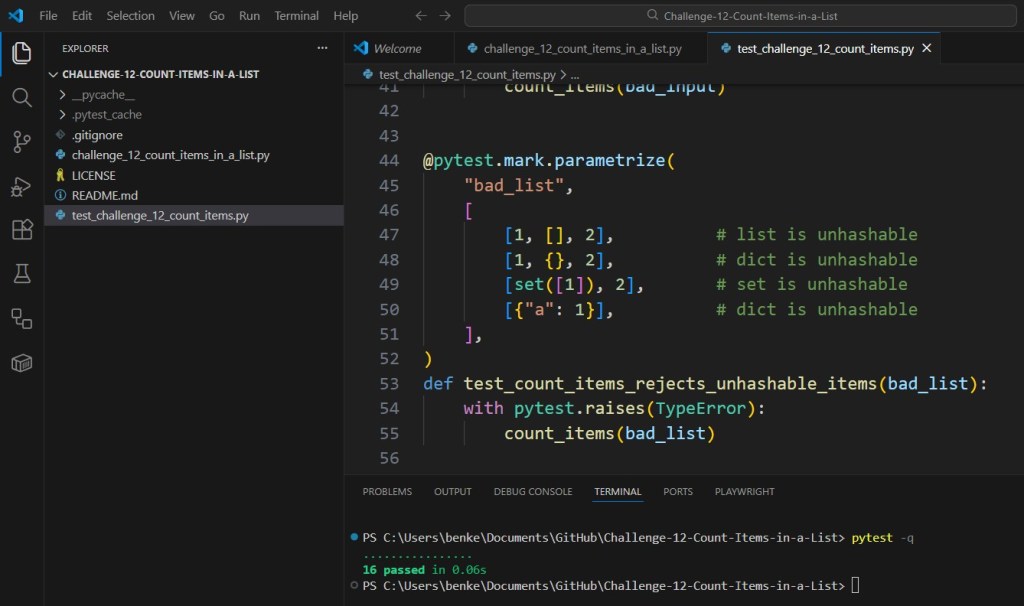
- Each item in the list must be hashable (so it can be used as a dictionary key).
- Return a dictionary where:
- Keys are the unique items
- Values are the number of times each item appears
- Return an empty dictionary for an empty list.
- Raise a
TypeErrorfor invalid input.
Examples
count_items([1, 2, 2, 3])
# → {1: 1, 2: 2, 3: 1}
count_items(["a", "b", "a"])
# → {"a": 2, "b": 1}
count_items([])
# → {}
Invalid Input Examples
count_items("abc") # TypeError
count_items(None) # TypeError
count_items([1, [], 2]) # TypeError (unhashable item)
Hints
- Use a dictionary to keep track of counts.
- Check whether an item already exists in the dictionary.
- Increment carefully.
What This Challenge Teaches
- Iterating through lists
- Using dictionaries as counters
- Understanding hashable vs unhashable types
- Writing predictable data-processing functions
Bonus Challenges
- Ignore case when counting strings
- Return items sorted by frequency
- Rebuild the solution using
collections.Counter - Count items across multiple lists
Why This Matters
Counting is one of the most common operations in programming.
Mastering this pattern gives you a reusable tool that applies to text processing, analytics, data validation, and more.
Beginner Track Checkpoint (Important)
With Challenge #12, your Beginner Track is now complete:
- Strings
- Lists
- Validation
- Conditionals
- Dictionaries
- Frequency patterns
This is a solid, real beginner foundation — not fluff.
🔗 View reference solution on GitHub
(After you’ve tried the challenge)
👉Next Challenge →
Want more practical Python challenges?
Subscribe to the Solve With Python newsletter and get new problems delivered to your inbox.